On Tuesday, 6th October, Federal Treasurer Josh Frydenberg handed down the 2020/21 Federal Budget, outlining a further $98 billion in financial economic support, however acknowledging a $200 billion deficit – the biggest since World War II.
Under the Federal Government’s economic recovery plan, Treasury highlighted its focus on delivering rapid action to help “build the Australian economy again and for the future”, ensuring economic growth opportunities for individual Australians & businesses, and support for industries heavily impacted by the global COVID-19 pandemic.
The 2020/21 Budget outlined the Government’s provision to introduce expedited tax relief and benefits to individual tax payers, heightened concessions for small & medium-sized businesses in addition to further support programs, job creation programs for young Australians, and investment in industry – such as Infrastructure, Manufacturing, Regional Tourism, Agriculture, Education, and Aged Care.
In this report, we breakdown the main measures released as part of the ‘Australian Federal Budget – 2020/21’.
Individuals
Lower Personal Income Tax & Tax Thresholds
This years’ Budget highlighted the delivery of additional Personal Income Tax relief designed to support individual Australians and strengthen economic recovery, as a result of impacts from COVID-19.
Announced by Treasury, the Government will bring forward ‘Stage Two’ of its Personal Income Tax Plan to 1 July 2020, alongside retaining the Low & Middle Income Tax Offset (LAMITO) for 2020/21.
Under the accelerated program (originally due FY2022/23), the announced changes are as follows:
- Top threshold of 19 per cent Personal Income Tax bracket will increase from $37,000 to $45,000;
- The Low Income Tax Offset (LITO) will increase from $445 to $700. The increased LITO will be withdrawn at a rate of 5 cents per dollar between taxable incomes of $37,500 and $45,000. The LITO will then be withdrawn at a rate of 1.5 cents per dollar between taxable incomes $45,000 and $66,667; and
- The top threshold of the 32.5 per cent Personal Income Tax bracket will increase from $90,000 to $120,000.
Additionally, the accelerated new Income Tax Thresholds coming into effect – retrospectively commencing from 1 July 2020 – are outlined below:
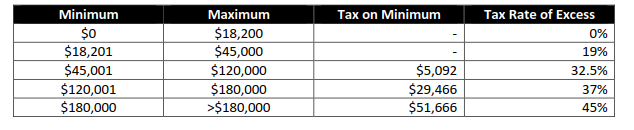
The above changes have now been legislated, following the pass of Royal Assent.
First Home Loan Deposit Scheme
The Federal Budget outlined further support will continue for Australians looking to purchase or build their first home through the additional allocation of 10,000 spots available within the ‘First Home Loan Deposit Scheme’.
The scheme enables first-home buyers to get into the market, by obtaining a loan to build a new home or purchase a newly built home with a deposit of 5 per cent. Under the Scheme, first-home buyers avoid the lenders’ mortgage insurance, with the Federal Government acting as ‘guarantor’ on the loan.
The additional guarantees will be available until 30 June 2021 and will drive more construction projects, and support jobs as part of the Federal Government Economic Recovery Plan.
Eligible first home buyers will also be able to take advantage of the Government’s ‘First Home Super Saver Scheme’ and ‘HomeBuilder’ program, and first home buyers may also be eligible for State and Territory grants and concessions.
Older Australians / Age Pensioners
The Federal Government is supporting older and disabled Australians and their families by providing a targeted Capital Gains Tax (CGT) exemption for granny flat arrangements where there is a formal written agreement in place.
Under the measure, CGT will not apply to the creation, variation or termination of a formal written granny flat arrangement providing accommodation for older Australians or people with disabilities.
The measure will commence as early as 1 July 2021.
This change will only apply to agreements that are entered into because of family relationships or other personal ties and will not apply to commercial rental arrangements.
Additionally, age pensioners will receive two additional economic support payments – one in December ($250) and the second in March ($250).
Businesses
Temporary Full Expensing
The 2020/21 Federal Budget announced the Government’s further support for businesses, providing companies with an aggregated turnover less than $5 billion, the ability to deduct the full cost of eligible capital depreciable assets acquired from 7:30PM AEDT on 6 October 2020 and first-used or installed by 30 June 2022.
Alongside this, the scheme outlines that the outright deduction may also be available for the cost of improvements to existing eligible depreciable assets during the full expensing period.
It is noted, small & medium-sized businesses (those with an aggregated annual turnover of less than $50m) can fully deduct second-hand assets purchased and installed during the eligible period.
Additionally, as part of the scheme, other considerations include:
- Larger business entities can still deduct the full cost of eligible second-hand assets costing less than $150,000 that are purchased by 31 December 2020, under the enhanced Instant Asset Write-Off;
- Businesses that acquired eligible assets for the pre-existing enhanced $150,000 Instant Asset Write-Off will have an extra six-months, until 30 June 2021, to first-use or install those assets; and
- Small businesses can deduct the balance of their simplified depreciation pool at the end of the Income Year while full expensing applies. The five-year limitation period where a small business entity opts out of this regime continue to remain suspended.
Loss Carry-Back Provisions
The Federal Government has announced the introduction of a ‘Loss Carry Back’ program for eligible companies – aimed at supporting previously profitable companies, who now find themselves in a loss position due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Under the program (which is now legislated), Corporate Tax entities with an aggregated turnover of less than $5 billion can apply tax losses in Income Years 2019/20, 2020/21 or 2021/22 against tax profits in a previous year; generating a refundable offset in the year in which the loss is made.
The tax refund would be limited by requiring that the amount carried back is not more than the earlier taxed profits and that the carry back does not generate a franking account deficit.
Additionally, the tax refund will be available on election by eligible businesses when they lodge their 2020-21 and 2021-22 Tax Returns.
The introduction of the program aims to give vital cash-flow to businesses that would have been profitable, but for strict lockdown and restrictions to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
Example

JobMaker – Hiring Credit Program
The 2020/21 Federal Budget highlighted the introduction of the JobMaker – Hiring Credit, aimed at building employment opportunities for young people and providing incentive for businesses to take on additional young job seekers.
From 7 October 2020, eligible employers will be able to claim a two-tier wage subsidy for every new employee aged between 16 – 35 years old hired for newly created employment positions, which increases the total employee headcount of the business. The two-tier payment structure is outlined as follows:
| New Employee Aged 16 - 29 | $200 / week |
| New Employee Aged 30 - 35 | $100 / week |
The payments will be available for the first 12-months of employment for any new jobs created until 6 October 2021, and employers will be required to make claims in arrears from 1 February 2021.
In order for an employee to be eligible, they must have been on JobSeeker, Youth Allowance or the Parenting Payment for at least one of the past three months. Additionally, employees must work an average of at least 20 hours a week over the reporting period, and begin their role between October 7, 2020 and October 6, 2021.
Boosting Apprentices – Wage Subsidy
Announced ahead of the Federal Budget, the Government has introduced the ‘Boosting Apprenticeship Commencements’ wage subsidy, focused on supporting businesses and Group Training Organisations to take on new apprentices and trainees.
Any business or Group Training Organisation that engages an Australian Apprentice on or after 5 October 2020 may be eligible for a subsidy of 50 per cent of wages paid to an apprentice between 5 October 2020 and 30 September 2021, to a maximum of $7,000 per quarter.
It is important to note that the subsidy is capped at 100,000 places, and is not available for any apprentice receiving any other form of Australian Government Wage Subsidy (e.g. Supporting Apprentices & Trainees or JobKeeper programs).
SME Business – Tax Concessions
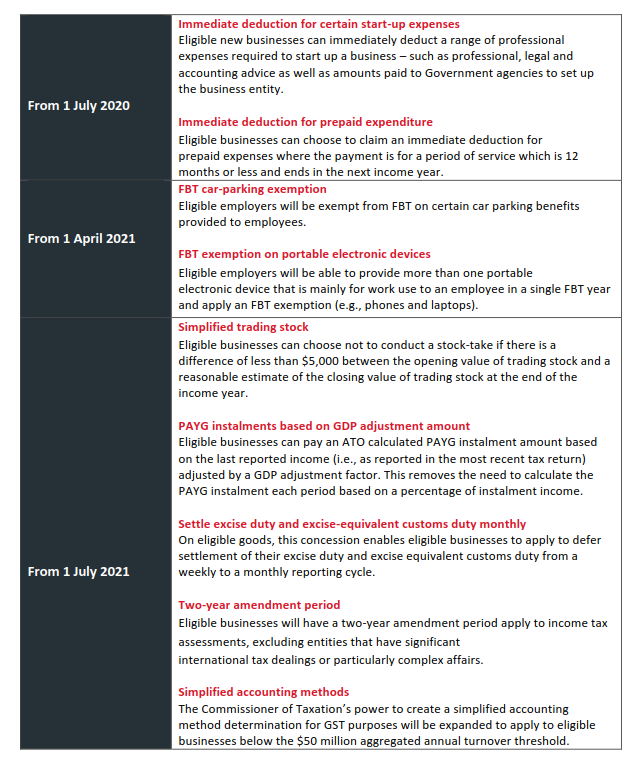
The Federal Government has announced businesses with an aggregated annual turnover between $10 million and $50 million will have access to up to ten (10) small business tax concessions.
We’ve summarised the Tax Concessions available to SME businesses in the table below (which have now been legislated):
Research & Development Tax Incentive - Enhanced Reforms
Under the Budget release, the Government announced changes to the R&D Tax Incentive (RDTI), proposed to take effect from 1 July 2021.
For small claimants (turnover less than $20 million), the Government will increase the refundable R&D Tax offest to 18.5% above the Corporate Tax rates, alongside removing the $4 million cap on annual cash refunds.
For larger claimants (turnover $20 million or more), the intensity test will be streamlined to two-tiers, and non-refundable R&D tax offset will be increased.
The Government will also proceed with the increase in the cap on eligible R&D expenditure from $100 million to $150 million per annum.
This measure has now been legislated, following Royal Assent.
FBT Exemptions
Fringe Benefit Tax exemptions were also announced by Treasury as part of this year’s Budget, whereby, certain employer-provided retraining and reskilling will be exempt from FBT - encouraging businesses to redeploy their workers to new roles within the business.
The Government is also to cut FBT compliance ‘red-tape’, allowing employers to use existing corporate records, rather than prescribed records, to complete their Fringe Benefit Tax return.
Additionally, as highlighted in the ‘SME Tax Concessions’ table previously, from 1 April 2021, eligible businesses will be exempt from the 47 per cent Fringe Benefit Tax on car-parking & multiple work-related portable electronic devices, such as phone or laptops, provided to employees.
Superannuation
The Federal Budget highlighted no changes to previously announced Superannuation measures – Superannuation Guarantee & COVID-19 temporary early release.
However, the commencement date for an increase in the maximum number of allowable members in SMSFs from four to six has been revised from 1 July 2019 to the date of Royal Assent of the enabling legislation. For more information on this, we will be releasing a further blog article covering the changes.
For More Information
For more information on 2020/21 Federal Budget and it will impact you, please contact your Archer Gowland Redshaw adviser on (07) 3002 2699 or (07) 3221 4004.
%20-%20HubSpot%20(1).png)
